
Estimating isn’t identical across sectors. Residential vs commercial estimating and civil estimating explained shows why methods shift with project scope, systems, and stakeholders. The right estimating methodology and cost planning improve accuracy, protect margins, and sharpen bids.
Understanding these construction estimating differences—and key differences in estimating methods—helps teams match approach to risk, compare types confidently, and win work with clarity.

Estimating methods change because each project type functions differently. A house, a high-rise, and a highway all require unique scopes, documentation, and cost inputs. The scale, design complexity, and accuracy demands vary—affecting how estimators plan, measure, and forecast costs for each project type.
Residential estimating is both simple and personal. Every home project reflects the owner’s vision, meaning estimators must balance accuracy with flexibility. The residential home estimating process focuses on clarity—using the right software tools, straightforward cost planning, and transparent documentation to create dependable, easy-to-understand estimates for small developments and houses.
Residential estimating starts with a clean, methodical process: reviewing drawings, performing detailed takeoffs, and building Bills of Quantities (BOQs) using software designed for small projects. This streamlined residential estimating workflow keeps things efficient while allowing room for quick updates when clients or designers adjust specifications mid-process.
Accuracy in residential estimating comes down to managing expectations. Homeowners often change materials or layouts, so estimators must plan allowances and track variations closely. Through good risk management and regular communication, estimators maintain cost accuracy in residential work while keeping the project budget realistic and transparent.
A small home initially estimated at $300,000 might end up costing $315,000 after material upgrades or design changes. This simple residential estimating example shows how early planning and precise cost control help keep budgets predictable and prevent unpleasant surprises once construction begins.
Commercial estimating is where complexity meets coordination. Large-scale, revenue-driven projects like offices, malls, and hospitals involve multiple systems and subcontractors. The commercial construction estimate focuses on multi-trade cost planning, strict timelines, and detailed documentation—ensuring every trade aligns with design, safety, and profitability goals.
Commercial projects bring together many systems—HVAC, MEP, structural, and finishing—that all require precise coordination. Each discipline needs its own takeoff, rate build-up, and section in the Bill of Quantities (BOQ). This level of commercial project design complexity demands deep technical understanding and a clear multi-system estimating workflow to avoid scope overlap or missed costs.
The tender process in commercial estimating is layered and competitive. Contractors must manage multiple bids from subcontractors, verify compliance documents, and align cost breakdowns with project specifications. Effective bid preparation across sectors ensures fair pricing, consistency, and transparency when handling subcontractor tendering across all major trades.
With so many trades involved, maintaining accuracy in estimating becomes critical. Estimators rely on digital takeoff verification tools, re-measurements, and peer cross-checks to ensure precision. This structured quality assurance in estimating minimizes rework, supports cost control, and helps deliver accurate, defendable estimates that protect both contractor margins and client trust.
Civil estimating focuses on scale, structure, and longevity. It forms the foundation for infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, and pipelines—where accuracy determines not just cost, but reliability for decades. The civil estimating process centers on data-driven planning, long-term budgeting, and strict compliance to public-sector standards.
Civil projects differ from other types because they prioritize function and durability over visual design. From highways and drainage networks to bridges and water systems, each job involves high design complexity and long execution timelines. Successful civil engineering estimation demands technical precision and deep understanding of infrastructure project cost types to keep the project functional, safe, and sustainable.
In civil works, budgets stretch across years, requiring robust cost forecasting and control systems. Estimators account for inflation, regulatory reviews, and evolving material prices. Detailed project budgeting in civil construction ensures transparency for stakeholders and smooth approval from government or funding agencies, while long-term cost forecasting keeps multi-year projects financially aligned from start to finish.
Every infrastructure project faces potential risks—environmental conditions, safety standards, and documentation errors can all affect cost and schedule. Skilled estimators manage these through thorough risk assessment, transparent tender documentation, and continuous cost accuracy checks. Maintaining strict compliance in civil estimating safeguards budgets, timelines, and public trust throughout project delivery.
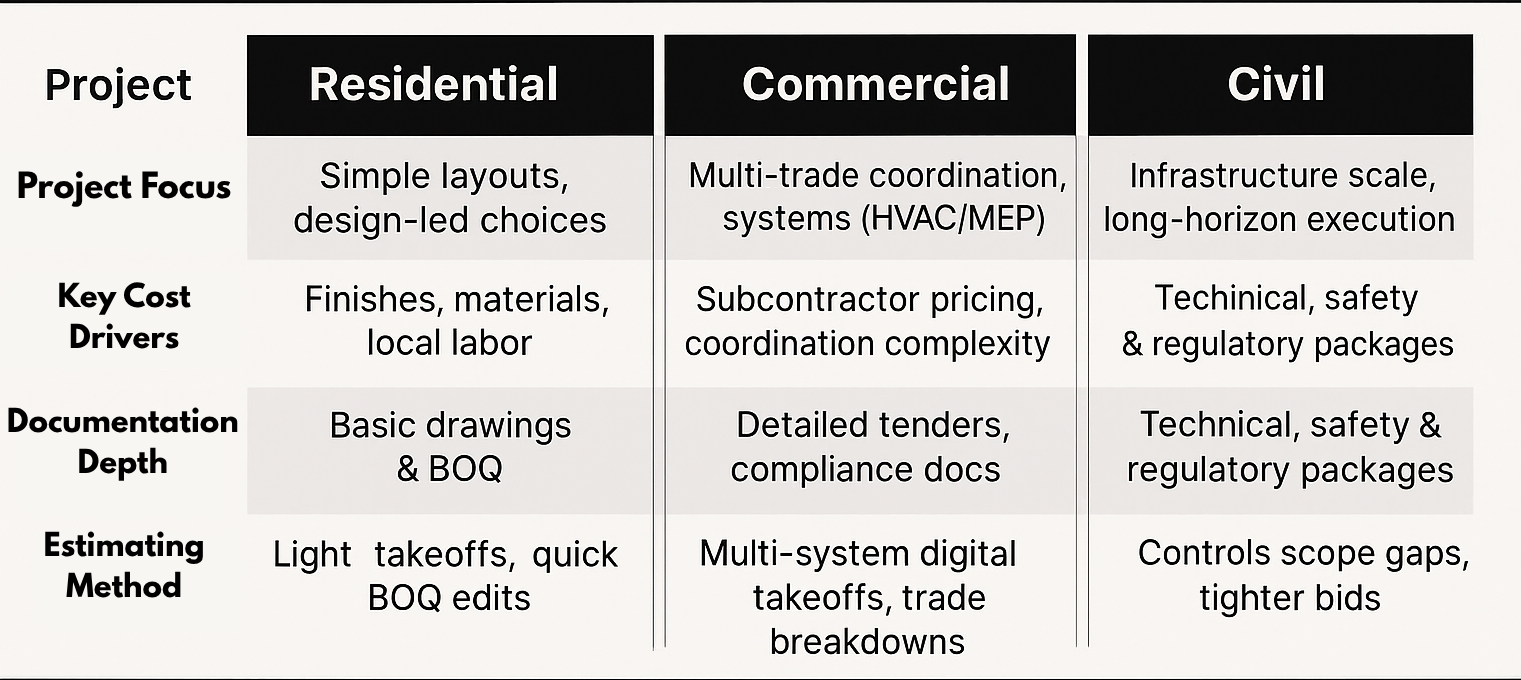
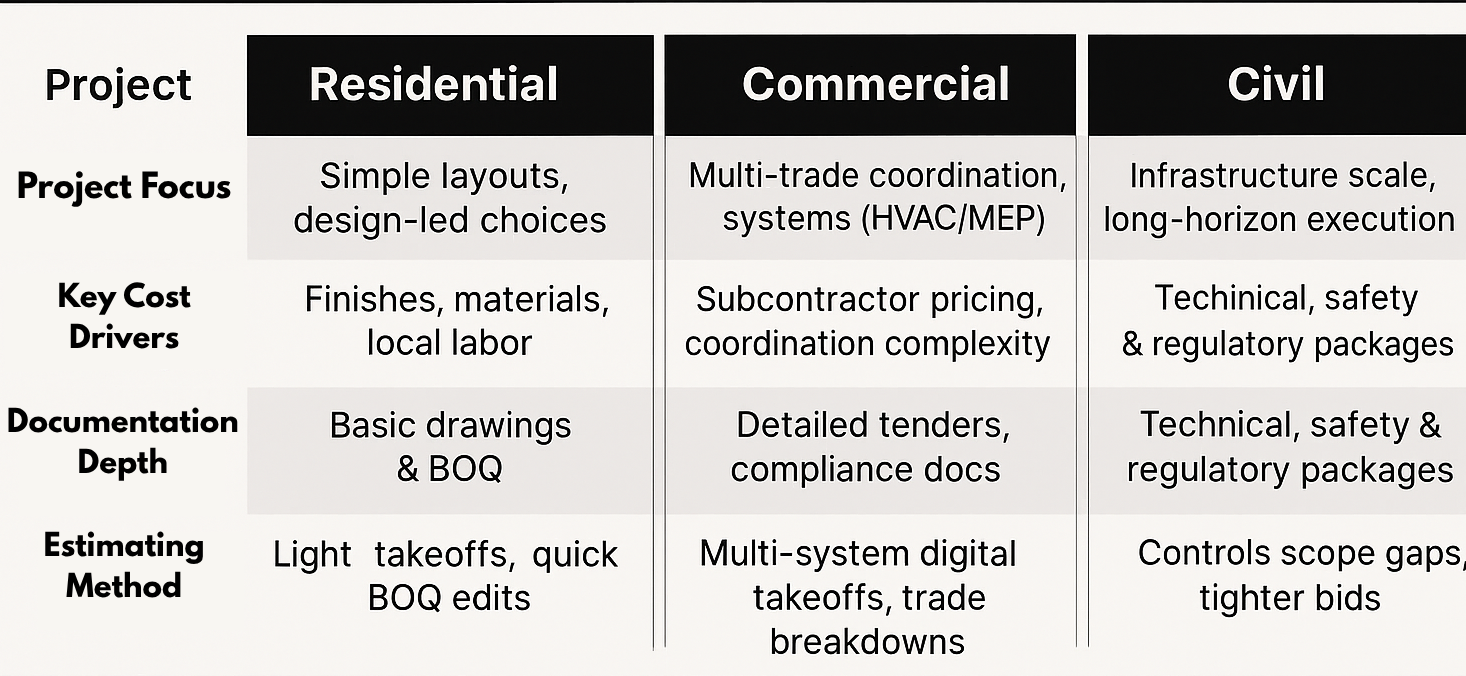
Cost Estimating approaches differ sharply across project types. A structured comparison helps builders, contractors, and clients understand how scope, documentation, timeframes, and risk evolve from residential to civil projects. This construction cost comparison by project type improves decision-making and ensures the right estimating methodology is used for each job.
|
Aspect |
Residential Estimating |
Commercial Estimating |
Civil Estimating |
|
Project Size & Scale |
Small to medium homes, personal builds |
Multi-storey offices, malls, institutions |
Large infrastructure — roads, bridges, utilities |
|
Project Scope |
Limited trades, simpler systems |
Multi-trade integration (HVAC, MEP, structure) |
Multiple layers — earthworks, utilities, public systems |
|
Documentation Level |
Basic drawings and BOQs |
Detailed BOQs, tender packages, compliance docs |
Complex design drawings, environmental and safety documentation |
|
Cost Drivers |
Material rates, design changes |
Subcontractor pricing, coordination complexity |
Equipment, bulk materials, environmental constraints |
|
Timeframe |
Short-term (weeks to months) |
Medium to long (months to a year) |
Long-term (multi-year projects) |
|
Risk & Complexity |
Low; driven by homeowner changes |
Moderate; coordination and scheduling risks |
High; weather, compliance, and scope variation risks |
|
Accuracy & Methodology |
Simplified estimating tools |
Multi-system digital takeoff software |
Detailed forecasting and cost control systems |
This estimating accuracy comparison highlights how each project type demands a tailored approach in methodology, documentation, and risk control.
Each sector can improve by borrowing strengths from others. Residential estimating can adopt the structured workflows seen in commercial projects. Commercial teams can integrate the forecasting discipline used in civil works. And civil estimators can enhance agility by simplifying reporting models. These cross-sector estimating insights drive continuous improvement, risk management, and better cost accuracy across the construction industry.
The differences between residential, commercial, and civil estimating go far beyond project size — they directly shape profitability, planning, and decision-making. When estimators tailor their approach to a project’s scope, complexity, and goals, they reduce risk, improve accuracy, and create stronger financial outcomes for both builders and clients.
Profit starts with precision. A well-prepared estimate protects margins by revealing the real cost before a project begins. In construction, even a small pricing mistake can turn a profit into a loss. By applying strong cost control and accurate forecasting, estimators can prevent overpricing, missed items, and rework. This attention to cost efficiency ensures every dollar is accounted for and every bid remains competitive.
Every project carries risk, but good estimating keeps it manageable. When estimators match their method to the project type, they avoid cost overruns, scope gaps, and approval delays. Effective risk management and cost planning make it easier to identify potential issues early—before they grow into expensive problems.
Modern estimating software tools are changing how the industry works. Whether it’s a small residential build or a large infrastructure project, digital takeoffs, templates, and shared platforms help estimators stay accurate and transparent. Choosing the right digital estimation tools for each sector improves consistency and saves valuable time during tendering and revisions.
Experienced estimators know that accuracy isn’t just about numbers — it’s about process, communication, and discipline. Real-world estimating depends on clear documentation, consistent reviews, and the right tools. These professional estimating insights help builders avoid mistakes and improve cost planning across every project type.
1. What is the main difference between residential, commercial, and civil estimating?
The main difference lies in the type and scale of projects being costed. Residential estimating focuses on homes, duplexes, and small developments, where details are simpler and costs are more predictable. Commercial estimating covers larger, more complex structures such as offices, malls, or hospitals that require advanced systems and higher accuracy. Civil estimating, on the other hand, deals with infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, and utilities, where costs are influenced by public standards, environmental factors, and heavy engineering requirements.
2. Why does the estimating process change across residential, commercial, and civil projects?
Each construction sector has unique project lifecycles, risk factors, and documentation standards. Residential estimating typically uses simpler templates and standard rates. Commercial projects demand detailed itemisation, subcontractor quotes, and compliance with mechanical, electrical, and structural systems. Civil estimating involves unit-rate costing, large-scale material quantification, and government-mandated specifications. The estimating process adapts to manage this complexity and reduce risk.
3. Which type of estimating is the most complex?
Civil estimating is generally the most complex because it involves large-scale public projects, variable site conditions, and significant regulatory oversight. Commercial estimating follows closely behind, especially when mechanical and electrical services are extensive. Residential estimating tends to be more straightforward but still requires careful consideration of finishes, materials, and local labour rates to maintain profit margins.
4. Why is understanding the difference between these estimating types important?
Knowing the difference helps estimators, builders, and clients align expectations. Using the wrong method can lead to underestimating costs, poor cash flow planning, and disputes during construction. Each estimating type requires its own data, accuracy level, and pricing model. Recognising this distinction ensures more reliable budgets and fewer financial surprises during project delivery.
5. Can one estimator handle residential, commercial, and civil projects together?
Yes, but only with specialised knowledge across each sector. A skilled estimator must understand the documentation, rate structures, and cost behaviour of every project type. While experience in one area helps, cross-sector estimating often requires advanced software, consistent benchmarking, and collaboration with engineers and project managers to achieve accuracy.
In understanding Residential vs Commercial vs Civil Estimating, one thing becomes clear: each project type demands its own balance of precision, planning, and control. When estimators apply the right estimating methodology to match a project’s scope, design complexity, and risks, the results show in every phase — from bid preparation to project completion.
Accurate estimating builds trust. It helps contractors bid with confidence, supports better client decisions, and keeps budgets realistic. Whether it’s a family home, a high-rise office, or a public infrastructure project, the goal remains the same — cost accuracy, efficient execution, and lasting project success. That’s why understanding these differences truly matters.